ovarian cyst biopsy|biopsy of ovarian cyst procedure : Tagatay In most cases, an ovarian biopsy takes place during the removal of a tumor in a surgical procedure such as a laparotomy or a laparoscopy. A . Tingnan ang higit pa We are kindling new fire! SHS Sneak Peek Don’t miss this one-time big-time exclusive event for incoming Grade 11 students of A.Y. 2024-2025! Register for free, bring your friends and win exciting prizes and giveaways as you plan your future.
ovarian cyst biopsy,In an image-guided biopsy, a doctor will use a CT scan or ultrasound to guide them on where to place a needle to take tissue samples from the ovaries or the omentum. An anesthetist will inject a local anesthetic under the skin over the area where the doctor will insert the needle. The doctor . Tingnan ang higit pa
In most cases, an ovarian biopsy takes place during the removal of a tumor in a surgical procedure such as a laparotomy or a laparoscopy. A . Tingnan ang higit paIf ovarian cancer causes ascites, which is a fluid buildup in the abdomen, a doctor can perform a paracentesis procedure to obtain a fluid sample to . Tingnan ang higit pa
This page was reviewed on November 23, 2021. An ovarian biopsy is a type of screening used to confirm whether you have ovarian cancer . During a .
ovarian cyst biopsy biopsy of ovarian cyst procedure Laparoscopy. A slim, lighted instrument (laparoscope) is inserted into your abdomen through a small cut (incision). Using the laparoscope, your provider can see .
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac in the ovarian tissue. The cyst may be unilocular or multilocular. The causes may be physiological, infectious, benign . Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of the different types of ovarian cysts. Outline the typical presentation and most .
Ovarian cysts are common. Most of the time, you have little or no discomfort, and the cysts are harmless. Most cysts go away without treatment within a .
Diagnostic tests. Biopsy for ovarian cancer. You may have a biopsy to help diagnose cancer of the ovary, fallopian tube or peritoneum. A doctor removes a small sample .

CT scans are not usually used to biopsy an ovarian tumor (see biopsy in the section "Other tests"), but they can be used to biopsy a suspected metastasis (area of spread). .An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac or pocket that forms on or inside an ovary. There are different kinds of ovarian cysts. They can occur for various reasons, and they may need .
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac. Most are benign, painless, and cause no symptoms. Discover different types, diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, and more. . Diagnosis. Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include: Pelvic exam. During a pelvic exam, your doctor inserts gloved fingers into your vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on your abdomen in order to feel (palpate) your pelvic organs. The doctor also visually examines your external genitalia, vagina and cervix.
An ovarian biopsy is a diagnostic test to determine if you have ovarian cancer. In very rare cases, if your doctor suspects you have ovarian cancer, he or she will remove the abnormal tumor and send the tissue to a lab to confirm the diagnosis. An ovarian biopsy that is performed as a standalone procedure can spread the cancerous cells and lead .
Results. This study identified 144 cases of ovarian masses sampled by aspiration or needle biopsy between 2000 and 2013. Ninety-two (64%) cases had corresponding histopathology, 84 (91%) of which were obtained concomitantly. On histology, 12 (13%) cases were malignant and 80 (87%) benign. Three false negative .
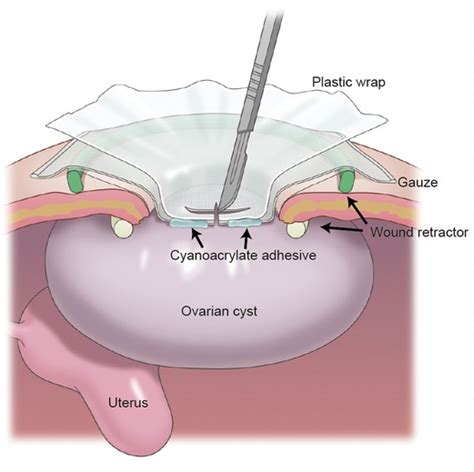
Biopsy procedure of ovarian cyst and uterus; symptoms and recovery after results. As a final resort, the cyst could also be removed if it's large to shrink or if it's either solid or stuffed with dust. The cyst can also be removed if it's inflicting a major quantity of pain and distress or if it's unendingly growing.

Symptoms. Most ovarian cysts cause no symptoms and go away on their own. But a large ovarian cyst can cause: Pelvic pain that may come and go. You may feel a dull ache or a sharp pain in the area below your bellybutton toward one side. Fullness, pressure or heaviness in your belly (abdomen). Bloating.
The adnexa is a set of structures adjacent to the uterus, consisting of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Even though the fallopian tubes are one of the major adnexal structures, this article will focus on the ovaries and the different types of cysts that can form within the ovary. The ovaries are suspended laterally to the uterus via the utero .
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovary ( figure 1 ). They are common and can happen at any age. Some people with ovarian cysts have pain or pelvic pressure, while others have no symptoms. Fortunately, most ovarian cysts do not require surgical removal and are not caused by cancer. Pelvic exam: Your provider will likely perform this test to feel the ovaries for cysts.; Ultrasound: Sound waves create images and can show the cyst's shape, size, and location.It can also determine if the ovarian cyst is filled with fluid or solid tissue. Hormone levels: Checking your estrogen levels help to determine if hormones caused the cyst.; .
ovarian cyst biopsy During laparoscopic surgery: A small incision is made in the abdomen to place a tiny camera and a separate small incision is made for the surgeon to insert an instrument with which to perform the procedure. The cyst is dissected off of the ovary, if possible (or the entire ovary may need to be removed). The cyst tissue is removed from the body.A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a small sample of body tissue so it can be examined under a microscope. A tissue sample can be taken from almost anywhere on or in your body, including the skin, organs and other structures. The term biopsy is often used to refer to both the act of taking the sample and the tissue sample itself.Abstract. Purpose: Image-guided needle biopsy represents a minimally invasive method for pathologic diagnosis of a mass. This study evaluates the diagnostic yield, accuracy, and safety of ovarian mass biopsy with combined core and fine-needle technique. Materials and methods: Medical records of all women at least 18 years of age, referred from .An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops on an ovary. They're very common and do not usually cause any symptoms. Most ovarian cysts occur naturally and go away in a few months without needing any treatment. The ovaries. The ovaries are 2 almond-shaped organs that are part of the female reproductive system. There's 1 on each side of . A pelvic MRI is often done to further evaluate cysts seen on other tests like ultrasound. Pelvic MRI can often characterize ovarian cysts and other lesions into risk categories for cancer. Some radiologists use a system called O-Rads for MRI. This is a way to report lesions from a score of 1 to 5. 1 being benign representing normal ovary and 5 .Your doctor may recommend a biopsy if they think you might have cancer. In a biopsy, a doctor takes a small amount of tissue from the area of the body where cancer may be present. The tissue is sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope for cancer cells by a specialist called a pathologist. Other tests can suggest that cancer is in the .
Punch biopsy. During a punch biopsy, a circular tool is used to remove a small section of your skin's deeper layers. Incisional biopsy. During an incisional biopsy, your provider uses a scalpel to remove a small area of skin. Whether you receive stitches to close the biopsy site depends on the amount of skin removed. Ovarian masses, ranging from benign cysts to malignant tumors, present complex diagnostic challenges in women's healthcare. . However, there are challenges associated with implementing liquid biopsy for ovarian masses. The levels of ctDNA in the bloodstream can be quite low, making detection more challenging, particularly in early . Adnexal cysts are a common incidental finding at US, CT, and MRI but have historically caused a diagnostic dilemma for determining when to follow up and how to manage them. Characteristic imaging features of simple adnexal cysts include a simple fluid collection with smooth walls and no solid or vascular components. Day-to-day . If complex ovarian cysts do cause symptoms, people may notice the following: pressure or bloating in the abdomen. general pain in the lower abdomen. vomiting or nausea if the cyst causes the .
ovarian cyst biopsy|biopsy of ovarian cyst procedure
PH0 · what size ovarian cysts should be removed
PH1 · ovary biopsy in the office
PH2 · ovarian cysts when to worry
PH3 · ovarian cyst warning signs
PH4 · ovarian cyst size chart
PH5 · can ovarian cysts turn cancerous
PH6 · biopsy of ovarian cyst procedure
PH7 · biopsy for ovarian cancer
PH8 · Iba pa